The health benefits of collagen
Collagen is the body’s most abundant protein making up at least a ⅓ of the protein in the human body. It is an important structural protein found predominantly in our bones, ligaments, tendons, connective tissues and skin, and plays a vital role in giving cohesion, elasticity, strength and structure. It is also essential for our overall health.
Collagen has long been known to support hair, skin, muscle, cartilage, ligament, blood-cell regeneration and the digestive system. What makes it so special is its essential amino acid profile: glycine, lysine, and proline that help regulate cell growth in every cell of the body, right down to the hair follicle, which is why people often report how thick their hair becomes on collagen supplementation.
Sally-Ann Creed’s famous Pure Hydrolysed Collagen is the best form of collagen you can get. Not only is it made from non-GMO, grass-fed cows, but it’s completely tasteless and odourless too! We’re so proud of our collagen and how it’s helped countless women (and men) across South African as they journey to wellness. If you’d like to learn more about this incredible collagen, then download our Ultimate Guide to Collagen. This handy guide contains everything you need to know about this incredible protein, and how it can benefit your hair, skin, nails, and joints.
Collagen and your skin

As your skin ages, its natural collagen breaks down, resulting in sagging skin.
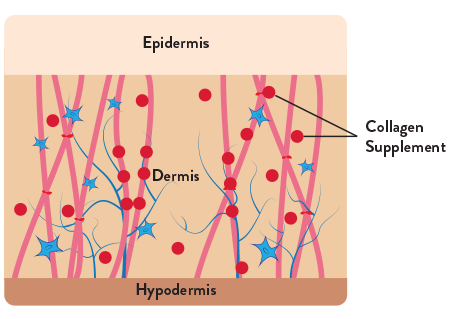
Supplemented collagen is absorbed into the bloodstream and deposited in the dermis, restoring existing collagen structures and plumping up the skin.
Our incredible non-GMO Pure Hydrolysed Collagen consists of 100% collagen peptides containing amino acids including proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline, considered to be essential components of collagen. These proteins help maintain the amount of collagen in the skin.
With collagen being so abundant in connective tissue, it comes as no surprise that it is a major component of your skin. The more collagen one has, the firmer, plumper, more hydrated your skin. But what exactly is the function of collagen in the skin? It provides a structural and support framework. It does this by helping skin cells adhere to one another, and in doing so provides strength and elasticity. It also assists with skin hydration due to collagen’s moisture absorption and retention properties.

Skin
Fibroblasts, which are connective tissue cells, produce and maintain collagen. As we age, the fibroblasts’ function becomes impaired, and collagen production decreases. Collagen becomes fragmented and more loosely dispersed. Because of this, it cannot provide the skin with the same strength and elasticity. Along with decreased levels of elastin, these changes lead to the characteristic signs of ageing – wrinkles, fine lines, skin sagging and a more dry complexion.

Joints
Cartilage is a rubber-like connective tissue that protects our joints. One of the main components of cartilage is collagen. With sub-optimal cartilage health, this may lead to increased inflammation and joint disorders such as osteoarthritis. In a review of 5 clinical studies, it was found that a 10g daily dose of collagen, for an average duration of 24 weeks, led to a significant improvement in joint pain and stiffness.

Hair
Keratin, the primary protein found in hair, requires many amino acids found in collagen. Proline is a large component of keratin and taking collagen leads to stronger, thicker, faster growth of overall hair. 70% of the dermis contains collagen and this is where the root of the hair follicle is found. Collagen results in optimal skin structure and function, which in turn allows the hair follicle to grow at its optimum, and leads to a strong, healthy root hair, and to stronger, healthier hair growth.

Nails
Nails are also made of keratin. Nail growth actually starts within the nail root, located underneath the cuticle. As ‘new’ nail cells are formed within the root, ‘old’ nail cells are pushed out, and harden and flatten creating the translucent nail structure, or nail plate, we are so used to seeing. Collagen contains proline, which is necessary for keratin production, but is also high in arginine. Arginine is needed to create the optimal conditions for nail growth in the form of nutrients and blood flow.
The Ultimate Guide to Collagen
You’ve heard about it, seen the products being advertised, and may even have a friend or family member supplementing with it, but you’re still not 100% sure why. Well, we’ve put together a fantastic guide that will break down this trending buzzword and help you understand exactly what it is, and why you should be taking it too.
What is it?
Collagen is an animal-based protein that has been found to make up to a third of the human body’s protein. It is a component of our muscles, skin, hair, nails, bone, ligaments and tendons, with studies confirming that it actually makes up to 70% of our joint cartilage. With collagen being the most abundant protein in not just humans but mammals, it is no wonder that it is often referred to as the ‘glue that holds everything together’. It is like the scaffolding that provides flexibility, strength and structure to our bodies.
To help you understand all the intricacies of our various collagens, we’ve put together an Ultimate Guide to Collagen that you can download. Click the button below to download our guide and learn all there is to know about this incredible protein.
The 3 main types of collagen

Bovine Collagen
Bovine collagen is a naturally occurring blend of Type 1 and 3 collagen. It is made by the extracting connective tissue from bovine (cow), which is then denatured by applying heat to form a gelatine. The gelatine then undergoes an enzymatic hydrolysis which produces a pure form of bovine collagen hydrolysate. This form of collagen is easily and readily available, absorbed and utilised by the human body.

Chicken Collagen
Chicken collagen is Type 2 collagen and is taken from the chicken sternum. It can help reduce pain and stiffness from osteoarthritis and support cartilage repair and regeneration. It’s the collagen of choice for arthritic complaints as well as back and neck pain caused by surgery. All collagen is anti-inflammatory, but chicken collagen is especially good for fighting bone and cartilage-related pain and inflammation.

Marine Collagen
Marine collagen is type 1 collagen. Many are wary of marine collagen because of the unethical production methods using jellyfish, sharks, sea cucumber and other marine animals. Our marine collagen is sourced from 100% wild caught, marine whitefish, and is Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) certified at source. This means that our marine collagen meets the MSC standard in terms of management and sustainability.
Some collagen companies sell products that contain multiple types of collagen mixed together. We don’t. We believe in serving only 100% pure natural products, and should dose each according to your body’s unique needs. That’s why we NEVER mix our collagens – you simply don’t know the ratios used in the mix, so you might not be getting the correct dosage required.

Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, plays a crucial role in promoting collagen absorption within the body. Collagen is a protein responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of skin, tendons, and cartilage. Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis as it acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in collagen production. Furthermore, vitamin C helps convert the precursor molecule, proline, into hydroxyproline, which is vital for collagen stability. Additionally, vitamin C has antioxidant properties that protect collagen from degradation by free radicals, preserving its youthful appearance. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin C through diet or supplements supports collagen absorption and benefits skin elasticity, joint health, and overall connective tissue strength.
Vitamin C plays a vital role in the absorption of collagen, and because of this,many other companies will mix vitamin C with their collagen. We don’t. We firmly believe that when taking vitamins, it’s best to dose as per your body’s unique requirements. That’s why we don’t add it to our Pure Hydrolysed Collagen, but rather recommend taking a separate vitamin C such as our EsterVit-C, Super Cee, or Scorbi-Cee
Other types of collagen
Gelatine
Although collagen and gelatine are very similar, they react differently. Gelatine turns into a gel similar to gel, whereas collagen does not. If you can’t afford collagen – you can always take gelatine and get similar results. That way I am able to get the best of both worlds.
Gelatine, like collagen, is excellent for cartilage and connective tissue – and does many of the things collagen does. Collagen is more easily absorbed but gelatine is still amazing – it’s what you find in bone broth which is such a game-changer.
Bone Broth
People have been making bone broth since the beginning of humankind. Anthropologists think people drank liquid infused with bones and other animal parts as early as prehistoric times. It’s a liquid made from boiling animal bones and connective tissue. Simmering the bones in water with some vinegar helps release nutrients from the marrow within the bones, as well as break down other tissues into the water. The result is a flavorful, nutritious broth.
Organic bone broth is rich in protein, collagen and key minerals. These vital nutrients are recognized for supporting a wide range of health benefits.It contains no known allergens, it is organic, and it contains essential amino acids that are easily absorbed in the human body.

Collagen has some incredible health benefits from less fine lines and wrinkles, and beautiful, firm skin right through to healing the gut, the joints, eyes and a dozen other things.
Collagen is naturally produced by your body – it’s the most abundant protein accounting for 30% of your body’s protein makeup. It’s what keeps your skin looking healthy and radiant, and is also responsible for your skin’s elasticity, preventing the lines and wrinkles. It is responsible for healthy hair, skin, nails, and connective tissue and enables the skin to “bounce back” into place. It prevents you from becoming frail along with your blood vessels and tendons. Collagen is VITAL.
Are your collagen levels on the decline? If so, you’ll notice fine lines/wrinkles, maybe aching joints, minor injuries heal slower, you’re developing gut problems, your bones and teeth are not that great – if this sounds familiar, you could be experiencing signs of a collagen deficiency. As you age, your body slows down production of collagen. This is common and natural, so try our grass-fed, non-GMO, 100% Pure Hydrolysed Collagen – your skin will thank you!
Common questions about collagen
- Optimal joint health
- Improved bone density
- Heart health
- Improved & healthy gut microbiome
- Improved muscle mass & recovery
- Firmer skin
- Thicker, fuller hair
- Stronger nails
We recommend that you take collagen as a daily supplement, aiming for the optimal daily dose of 6g – 12g of collagen per day. The body will not absorb any more than this, and is deemed redundant.
No you don’t. In fact, research shows that doing this when first taking collagen could lead to very bad constipation and intestinal distress!
Some brands recommend taking SIX TABLESPOONS PER DAY (3 times the usual dosage) for 30 days in order to “collagen load”, much like “carbo loading” was recommended a few years ago. Doing this will immediately add up to 35g of additional protein to your diet. This amount of additional protein added so quickly can be detrimental to some such as those on reduced protein diets for renal disease (and to your wallet). There are in fact no credible studies to prove that “collagen loading” has any benefit whatsoever. All the science points to the fact that 10-15g is the optimal daily amount of collagen.
That’s why we advocate for starting slowly when it comes to collagen. We recommend starting with only 1 Tbsp (6g) of collagen per day for 2 weeks—to introduce your body to collagen in a safe and controlled manner. This will allow your gut to come to terms with the additional protein, preventing constipation and uncomfortable blockages. As your body gets used to our wonderful collagen, you can then increase your dosage to 2 Tbsp (12g) per day, which, according to modern science, is the optimal dosage for collagen.
Our collagen is easily digested, highly soluble, and extremely versatile. It can be used in just about anything from a hot cup of coffee, to an ice-cold smoothie or even your overnight oats. All you need is 1-2 scoops / TBSP / sachets of our collagen added to your daily routine to reap the amazing benefits. We usually recommend Type I and III (bovine) collagen not be taken together with Type II (chicken) collagen as they tend to compete for absorption in the gut, and this could hinder optimal absorption of either products, therefore they should be taken at different times of the day.
Anything from 2 weeks to 3 months. We recommend a daily consumption of the recommended dosage for at least 8 weeks.
Yes, you can. We advise that you take just 1 sachet or tablespoon per day.
While it may be safe for children, we always recommend that you focus on a wholesome diet before introducing any form of supplementation. Children’s bodies are still developing and their liver may take strain trying to process additional protein supplementation. It is advisable to only start taking collagen from the age of 24 years.
Our Sally-Ann Creed® Pure Hydrolysed Collagen is Halaal certified. It is also Kosher certified at source and our contract packers are certified too.
- James McIntosh. Medically reviewed by Reema Patel, MPA, PA-C. Updated June 2022. What is Collagen, and why do people use it? Medical News Today. Online: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/262881
- Jillian Kubala, MS, RD. Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R.D., CDE, Nutrition. Updated February 2022. What is collagen, and what is it good for? Healthline. Online: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/collagen
- David Goodsell. April 2000. Molecule of the month: Collagen. RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB) online: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2000_4
- Andrew M Holwerda, Luc J C van Loon, The impact of collagen protein ingestion on musculoskeletal connective tissue remodeling: a narrative review, Nutrition Reviews, Volume 80, Issue 6, June 2022, Pages 1497–1514, https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab083
- Gauza-Włodarczyk M, Kubisz L, Włodarczyk D. Amino acid composition in determination of collagen origin and assessment of physical factors effects. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Nov;104(Pt A):987-991. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 4. PMID: 28687386. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28687386/
- G. van de Walle, MS RD. December 2018. Top 9 Benefits and uses of Glycine. Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/glycine
- Marlyn Wu, Kelly Cronin, Jonathan S. Crane. 2022. Biochemistry, Collagen Synthesis. StatPearls, National Library of Medicine https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507709/
- Khatri, M., Naughton, R.J., Clifford, T. et al. The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review. Amino Acids 53, 1493–1506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03072-x
- Nezwek TA, Varacallo M. Physiology, Connective Tissue. [Updated 2022 Sep 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542226/
- Protection of gastric mucosal integrity by gelatin and simple proline-containing peptides, Pathophysiology, Volume 7, Issue 1, 2000, Pages 69-73, ISSN 0928-4680, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-4680(00)00045-6.




