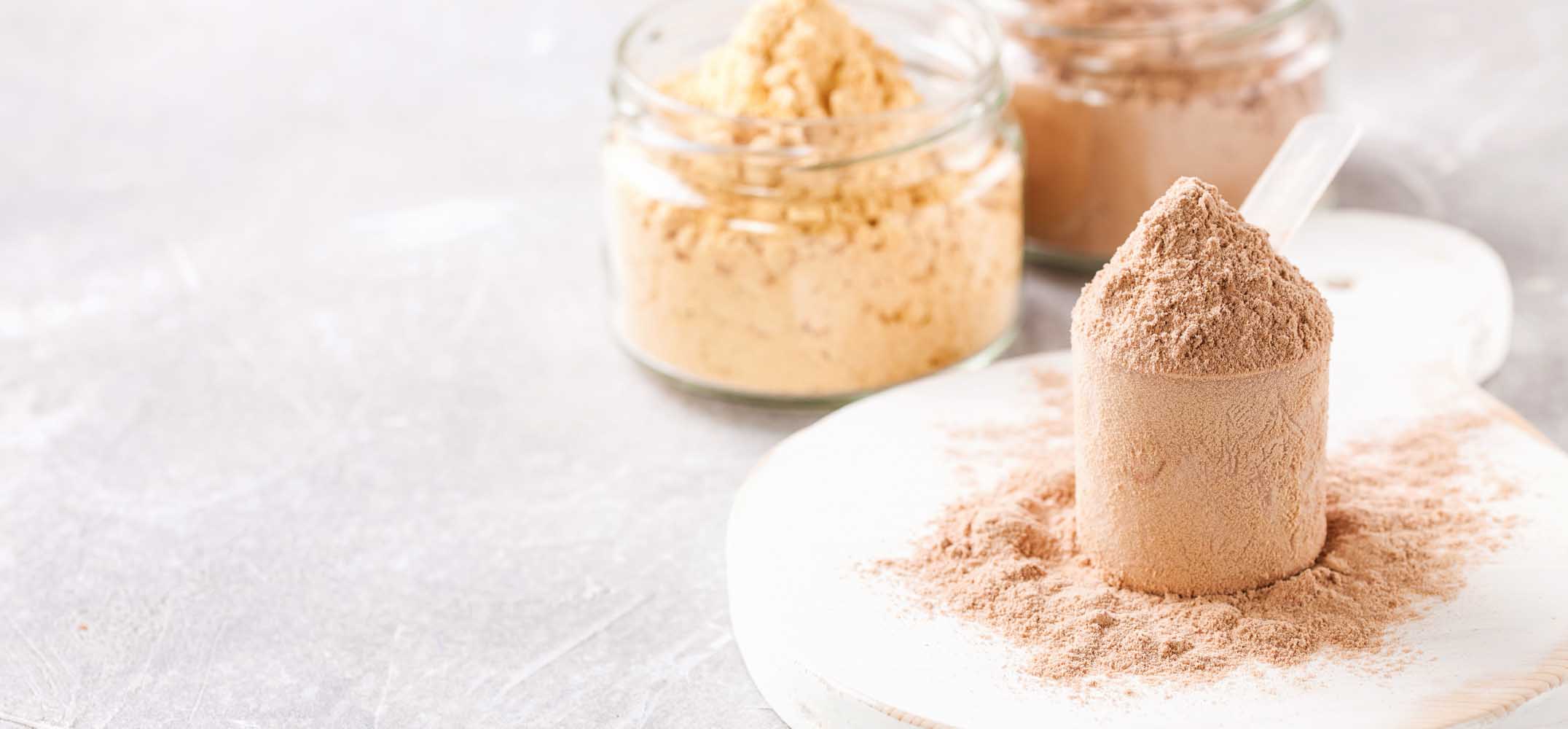
In the world of fitness and nutrition, protein is often hailed as the king of nutrients. It plays a crucial role in muscle repair, immune function, and overall well-being. Among the various sources of protein, whey protein stands out as a popular and effective option. However, not all whey proteins are created equal. In this article, we will explore the key differences between two common forms of whey protein: whey protein concentrate and whey protein isolate. Our goal is to help you make an informed choice that aligns with your health and fitness goals.
Understanding Whey Protein
Before delving into the differences, let’s first understand what whey protein is and why it’s valued in the nutrition and fitness community.
Derived from milk during the cheese-making process, whey protein is a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids necessary for optimal bodily function. It boasts an impressive amino acid profile, with a particularly high concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which play a pivotal role in muscle protein synthesis and recovery. Furthermore, whey protein is rapidly absorbed by the body, making it an ideal choice for post-workout nutrition.
Now, let’s explore the two main forms of whey protein: concentrate and isolate.
Whey Protein Concentrate: A Closer Look
Whey Protein Concentrate typically contains around 70-80% protein by weight. The remaining 20-30% consists of carbohydrates (lactose) and fats. While it does provide a decent protein content, it may not be suitable for individuals looking to increase their protein intake without additional calories.
The benefits of whey protein concentrate include:
- Nutrient-rich: Whey protein concentrate retains many of the beneficial nutrients found in whole whey, such as immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which support the immune system.
- Cost-effective: Whey protein concentrate tends to be less expensive than whey protein isolate due to its lower level of processing.
- Satiety: The presence of fats and carbohydrates in Whey protein concentrate can help you feel fuller for longer, making it a good option for meal replacements or weight management.
However, there are some downsides to whey protein concentrate:
- If you are lactose intolerant or have a sensitivity to lactose, Whey protein concentrate may not be the best choice for you, as it contains a higher amount of lactose compared to whey protein isolate.
- The lower protein concentration in Whey protein concentrate means you need to consume more product to achieve the same protein intake as with whey protein isolate.
Whey Protein Isolate: The Purest Form
Whey protein isolate undergoes additional processing steps to remove most of the fats, lactose, and other non-protein components, resulting in a product that is typically 90% or more pure protein. This high level of purity makes whey protein isolate an attractive option for those seeking a protein source with minimal additional nutrients.
The benefits of whey protein isolate include:
- High protein content: With over 90% protein content, Whey protein isolate is an excellent choice for those looking to increase their protein intake without added fats and carbohydrates.
- Low lactose: The extensive filtration process used to produce Whey protein isolate reduces lactose content to minimal levels, making it a suitable option for many individuals with lactose intolerance.
- Rapid absorption: Whey protein isolate is quickly digested and absorbed, making it an ideal choice for post-workout recovery when your muscles need protein most.
- Low fat and carbs: Whey protein isolate is virtually fat-free and contains very few carbohydrates, making it suitable for those on low-carb or ketogenic diets.
However, it’s important to consider the downsides of whey protein isolate:
- Whey protein isolate is generally more expensive than whey protein concentrate due to the additional processing steps.
- The extensive processing to create Whey protein isolate removes some of the beneficial nutrients found in whole whey, such as immunoglobulins and lactoferrin.
Now that we’ve explored the differences between whey protein concentrate and whey protein isolate, let’s discuss the best choice for your unique needs.
- If you are lactose intolerant or have lactose sensitivity: Whey protein isolate is the clear winner here. Its minimal lactose content makes it easier to digest and less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
- If you’re looking for the highest protein content: Whey protein isolate is your best bet. With over 90% pure protein, it allows you to maximise your protein intake without extra calories from fats and carbs.
- If you’re on a tight budget: Whey protein concentrate is a more cost-effective option, providing a good balance of protein and additional nutrients. While it may not be as pure as isolate, it’s still a valuable source of protein.
- If you’re seeking immune support and additional nutrients: Whey protein concentrate retains more of the natural immune-boosting components found in whole whey, making it a suitable choice if you want a holistic approach to your nutrition.
In the debate between whey protein concentrate and whey protein isolate, the scales tip overwhelmingly in favour of whey protein isolate for several reasons:
- Higher Protein Content: Whey protein isolate contains over 90% pure protein by weight, providing a more efficient way to meet your protein goals without unnecessary calories from carbohydrates and fats.
- Lactose-Free: Isolate is virtually lactose-free, making it suitable for those with lactose intolerance.
- Minimal Fat Content: It is a low-fat option, ideal for individuals aiming to limit their fat intake.
- Superior Digestibility: Isolate is highly digestible and less likely to cause digestive discomfort or allergic reactions.
- Bioavailability: Its rapid absorption rate makes it the top choice for post-workout recovery and muscle protein synthesis.
If you’re looking for a pure, clean whey protein, then Sally-Ann Creed Pure Whey Isolate is what you’re after. Its purity and quick digestibility make it an ideal choice for post-workout recovery and meeting your protein requirements efficiently. Remember, the best choice for you is the one that aligns with your dietary preferences, lifestyle, and health considerations. Always consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist to ensure that your protein choice supports your overall well-being and fitness goals.